Biofermentation Process
Our proprietary biofermentation process sets us apart.
By harnessing the natural capabilities of bacteria used as cell factories, we produce highly specific blood group antigen ligands.
This method mimics enzymatic synthesis but is managed by bacteria, enhancing efficiency and allowing large scale production.
Advantages
One of the main advantages of biofermentation is its ability to produce complex glycans such as blood group antigen ligands with high specificity and consistency.
Unlike chemical synthesis, which can be labor-intensive and less precise, biofermentation leverages the natural biosynthetic machinery of bacteria to achieve
efficient and reproducible glycan production.
In summary, biofermentation is a powerful and versatile method for producing glycans.
By utilizing bacteria to manage the synthesis, this process offers a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional methods, providing high-quality glycans for various industrial and medical applications.
More details about GlycoBAR production process:
Biofermentation is a sophisticated and efficient method for producing oligosaccharides, which are essential sugar molecules involved in various biological processes.
Unlike traditional chemical synthesis or enzymatic methods, biofermentation uses living organisms, typically bacteria, to synthesize these complex molecules.
Here’s a detailed explanation of how biofermentation works in
producing antigens:
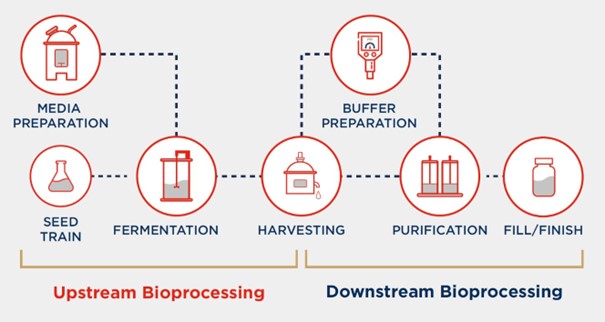

Selection and Cultivation of Bacteria:
The biofermentation process begins with the design of appropriate bacterial strains.
Designing a bacterial strain to produce a specific glycan involves genetic engineering.
The modified bacteria are cultured in controlled conditions with an optimized nutrient medium to enhance glycan production.
Through trial and optimization, the most efficient bacterial strain is selected for large-scale glycan production.
Once selected, the bacteria are cultivated in a controlled environment, which is typically a bioreactor.
The bioreactor provides optimal conditions for bacterial growth,
including the right temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient supply.
Nutrient Supply and Growth Medium.
The growth medium in the bioreactor contains all the necessary nutrients required for bacterial growth and glycan production.
This medium often includes a carbon source (such as glucose), nitrogen, vitamins, minerals, and other essential growth factors.
The composition of the growth medium is carefully formulated to maximize the production of the desired glycans.
Metabolic Pathways and Glycan Synthesis
Once the bacteria are actively growing in the bioreactor, they begin to synthesize glycans as part of their normal metabolic activities.
Bacteria have specific metabolic pathways that allow them to assemble glycan molecules from sugar precursors (which, in GlycoBAR case is a complex and difficult to produce precursor).
These pathways involve a series of enzymatic reactions where enzymes within the bacteria catalyze the addition of sugar units to growing glycan chains.


Regulation and Optimization:
The biofermentation process is closely monitored and regulated to ensure optimal glycan production. Factors such as nutrient levels, oxygen supply, and growth conditions are continuously adjusted to maintain the best possible environment for bacterial activity.
Harvesting and Purification
After a period of biofermentation, during which the bacteria have produced the desired glycans, the next step is to harvest and purify these molecules.
The bacterial culture is typically separated from the biofermentation broth through centrifugation or filtration.
The supernatant, which contains the glycans, is then subjected to various purification processes to isolate the glycans from other bacterial by-products.
These purification steps include chromatography, precipitation, and dialysis.
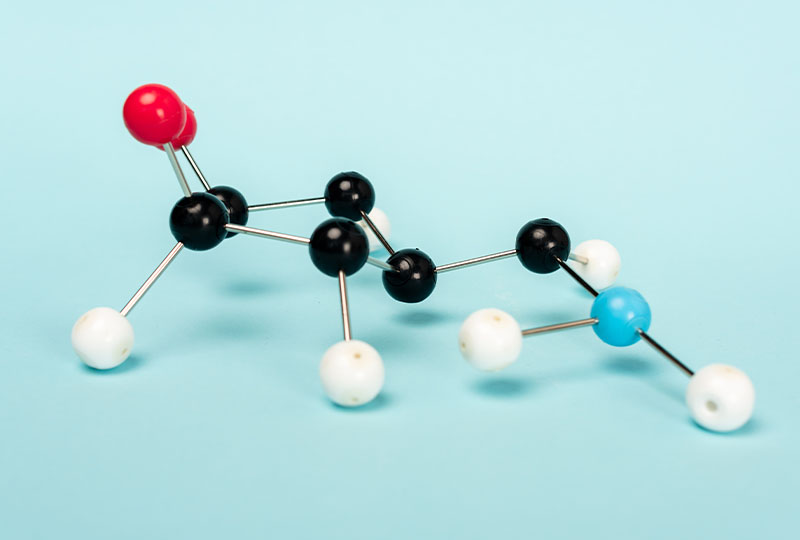


What’s an antigen ligand ?
From an antigen to a ligand : a spacer arm with an amine termination is added to the antigen so that it becomes a ligand with the appropriate geometry.
The ligands offers a greater antibody affinity and an easier coupling for customers.
Quality Control and Analysis
Each step of GlycoBAR process involves rigorous quality control and analysis.
The purified glycans are analyzed using advanced techniques such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and high- performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to confirm their structure and purity.
This ensures that the glycans meet the required specifications for their intended applications.

